pydase (Python Data Service)
pydase is a Python library for creating data service servers with integrated web and RPC servers. It's designed to handle the management of data structures, automated tasks, and callbacks, and provides built-in functionality for serving data over different protocols.
- Features
- Installation
- Usage
- Understanding Service Persistence
- Understanding Tasks in pydase
- Understanding Units in pydase
- Documentation
- Contributing
- License
Features
- Integrated web interface for interactive access and control of your data service
- Support for
rpycconnections, allowing for programmatic control and interaction with your service - Saving and restoring the service state for service persistence
- Automated task management with built-in start/stop controls and optional autostart
- Support for units
- Event-based callback functionality for real-time updates
- Support for additional servers for specific use-cases
Installation
Install pydase using poetry:
poetry add git+https://github.com/tiqi-group/pydase.git
or pip:
pip install git+https://github.com/tiqi-group/pydase.git
Usage
Using pydase involves three main steps: defining a DataService subclass, running the server, and then connecting to the service either programmatically using rpyc or through the web interface.
Defining a DataService
To use pydase, you'll first need to create a class that inherits from DataService. This class represents your custom data service, which will be exposed via RPC (using rpyc) and a web server. Your class can implement class / instance attributes and synchronous and asynchronous tasks.
Here's an example:
from pydase import DataService
class Device(DataService):
_current = 0.0
_voltage = 0.0
_power = False
@property
def current(self):
# run code to get current
return self._current
@current.setter
def current(self, value):
# run code to set current
self._current = value
@property
def voltage(self):
# run code to get voltage
return self._voltage
@voltage.setter
def voltage(self, value):
# run code to set voltage
self._voltage = value
@property
def power(self):
# run code to get power state
return self._power
@power.setter
def power(self, value):
# run code to set power state
self._power = value
def reset(self):
self.current = 0.0
self.voltage = 0.0
In the above example, we define a Device class that extends DataService. We define a few properties (current, voltage, power) and their getter and setter methods.
Running the Server
Once your DataService is defined, you can create an instance of it and run the server:
from pydase import Server
# ... defining the Device class ...
if __name__ == "__main__":
service = Device()
Server(service).run()
This will start the server, making your Device service accessible via RPC and a web server at http://localhost:8001.
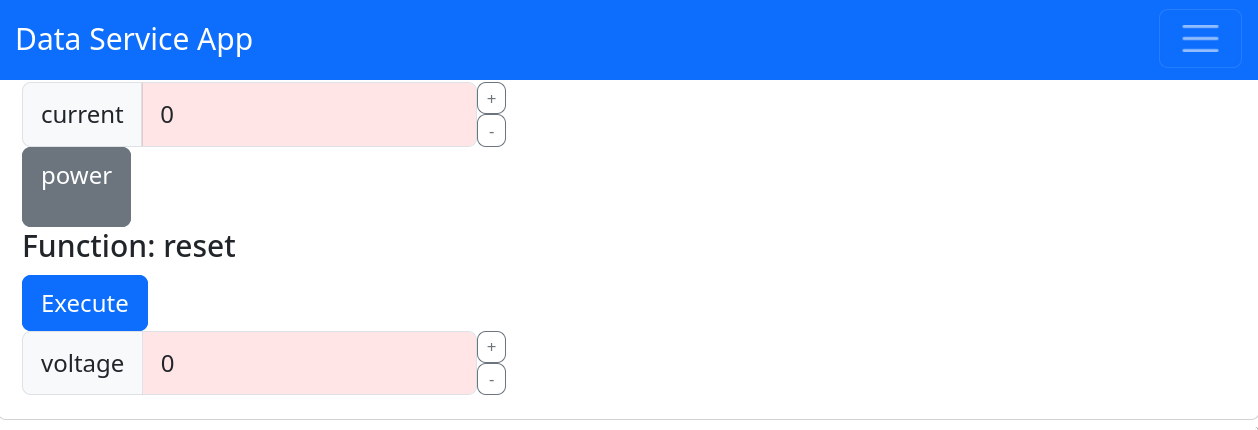
Accessing the Web Interface
Once the server is running, you can access the web interface in a browser:
In this interface, you can interact with the properties of your Device service.
Connecting to the Service using rpyc
You can also connect to the service using rpyc. Here's an example on how to establish a connection and interact with the service:
import rpyc
# Connect to the service
conn = rpyc.connect("<ip_addr>", 18871)
client = conn.root
# Interact with the service
client.voltage = 5.0
print(client.voltage) # prints 5.0
In this example, replace <ip_addr> with the IP address of the machine where the service is running. After establishing a connection, you can interact with the service attributes as if they were local attributes.
Understanding Service Persistence
pydase allows you to easily persist the state of your service by saving it to a file. This is especially useful when you want to maintain the service's state across different runs.
To save the state of your service, pass a filename keyword argument to the __init__ method of the DataService base class. If the file specified by filename does not exist, the service will create this file and store its state in it when the service is shut down. If the file already exists, the service will load the state from this file, setting the values of its attributes to the values stored in the file.
Here's an example:
from pydase import DataService, Server
class Device(DataService):
def __init__(self, filename: str) -> None:
# ... your init code ...
# Pass the filename argument to the parent class
super().__init__(filename=filename)
# ... defining the Device class ...
if __name__ == "__main__":
service = Device("device_state.json")
Server(service).run()
In this example, the state of the Device service will be saved to device_state.json when the service is shut down. If device_state.json exists when the service is started, the service will restore its state from this file.
Note: If the service class structure has changed since the last time its state was saved, only the attributes that have remained the same will be restored from the settings file.
Understanding Tasks in pydase
In pydase, a task is defined as an asynchronous function contained in a class that inherits from DataService. These tasks usually contain a while loop and are designed to carry out periodic functions.
For example, a task might be used to periodically read sensor data, update a database, or perform any other recurring job. The core feature of pydase is its ability to automatically generate start and stop functions for these tasks. This allows you to control task execution via both the frontend and an rpyc client, giving you flexible and powerful control over your service's operation.
Another powerful feature of pydase is its ability to automatically start tasks upon initialization of the service. By specifying the tasks and their arguments in the _autostart_tasks dictionary in your service class's __init__ method, pydase will automatically start these tasks when the server is started. Here's an example:
from pydase import DataService, Server
class SensorService(DataService):
def __init__(self):
self.readout_frequency = 1.0
self._autostart_tasks = {"read_sensor_data": ()} # args passed to the function go there
super().__init__()
def _process_data(self, data: ...) -> None:
...
def _read_from_sensor(self) -> Any:
...
async def read_sensor_data(self):
while True:
data = self._read_from_sensor()
self._process_data(data) # Process the data as needed
await asyncio.sleep(self.readout_frequency)
if __name__ == "__main__":
service = SensorService()
Server(service).run()
In this example, read_sensor_data is a task that continuously reads data from a sensor. The readout frequency can be updated using the readout_frequency attribute.
By listing it in the _autostart_tasks dictionary, it will automatically start running when Server(service).run() is executed.
As with all tasks, pydase will also generate start_read_sensor_data and stop_read_sensor_data methods, which can be called to manually start and stop the data reading task.
Understanding Units in pydase
pydase integrates with the pint package to allow you to work with physical quantities within your service. This enables you to define attributes with units, making your service more expressive and ensuring consistency in the handling of physical quantities.
You can define quantities in your DataService subclass using pydase's units functionality. These quantities can be set and accessed like regular attributes, and pydase will automatically handle the conversion between floats and quantities with units.
Here's an example:
from typing import Any
from pydase import DataService, Server
import pydase.units as u
class ServiceClass(DataService):
voltage = 1.0 * u.units.V
_current: u.Quantity = 1.0 * u.units.mA
@property
def current(self) -> u.Quantity:
return self._current
@current.setter
def current(self, value: Any) -> None:
self._current = value
if __name__ == "__main__":
service = ServiceClass()
# You can just set floats to the Quantity objects. The DataService __setattr__ will
# automatically convert this
service.voltage = 10.0
service.current = 1.5
Server(service).run()
In the frontend, quantities are rendered as floats, with the unit displayed as additional text. This allows you to maintain a clear and consistent representation of physical quantities across both the backend and frontend of your service.
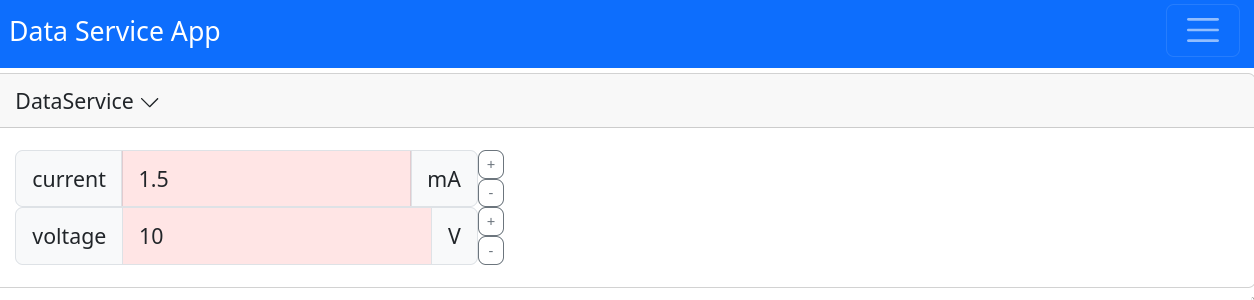
Should you need to access the magnitude or the unit of a quantity, you can use the .m attribute or the .u attribute of the variable, respectively. For example, this could be necessary to set the periodicity of a task:
import asyncio
from pydase import DataService, Server
import pydase.units as u
class ServiceClass(DataService):
readout_wait_time = 1.0 * u.units.ms
async def read_sensor_data(self):
while True:
print("Reading out sensor ...")
await asyncio.sleep(self.readout_wait_time.to("s").m)
if __name__ == "__main__":
service = ServiceClass()
Server(service).run()
For more information about what you can do with the units, please consult the documentation of pint.
Documentation
The full documentation provides more detailed information about pydase, including advanced usage examples, API references, and tips for troubleshooting common issues. See the full documentation for more information.
Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for details on how to contribute.
License
pydase is licensed under the MIT License.