pydase (Python Data Service)
pydase is a Python library for creating data service servers with integrated web and RPC servers. It's designed to handle the management of data structures, automated tasks, and callbacks, and provides built-in functionality for serving data over different protocols.
Features
- Integrated web and RPC servers
- Automated task management
- Event-based callback functionality for real-time updates
- Built-in support for serving data over different protocols
- Support for additional servers for specific use-cases
Installation
Install pydase using poetry:
poetry add git+https://github.com/tiqi-group/pydase.git
or pip:
pip install git+https://github.com/tiqi-group/pydase.git
Usage
Using pydase involves two main steps: defining a DataService subclass and then running the server.
Defining a DataService
To use pydase, you'll first need to create a class that inherits from DataService. This class represents your custom data service, which will be exposed via RPC (using rpyc) and a web server. Your class can implement class / instance attributes and synchronous and asynchronous tasks.
Here's an example:
from pydase import DataService
class Device(DataService):
_current = 0.0
_voltage = 0.0
_power = False
@property
def current(self):
# run code to get current
return self._current
@current.setter
def current(self, value):
# run code to set current
self._current = value
@property
def voltage(self):
# run code to get voltage
return self._voltage
@voltage.setter
def voltage(self, value):
# run code to set voltage
self._voltage = value
@property
def power(self):
# run code to get power state
return self._power
@power.setter
def power(self, value):
# run code to set power state
self._power = value
def reset(self):
self.current = 0.0
self.voltage = 0.0
In the above example, we define a Device class that extends DataService. We define a few properties (current, voltage, power) and their getter and setter methods.
Running the Server
Once your DataService is defined, you can create an instance of it and run the server:
from pydase import Server
# ... defining the Device class ...
if __name__ == "__main__":
service = Device()
Server(service).run()
This will start the server, making your Device service accessible via RPC and a web server at http://localhost:8001.
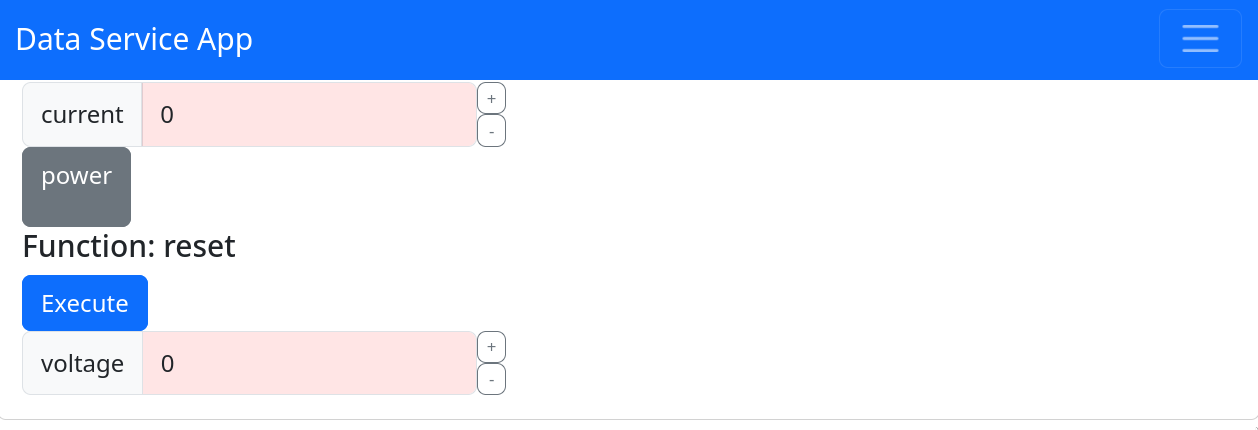
Accessing the Web Interface
Once the server is running, you can access the web interface in a browser:
In this interface, you can interact with the properties of your Device service.
Documentation
For more details about usage and features, see the full documentation.
Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for details on how to contribute.
License
pydase is licensed under the MIT License.